Cardiac Cycle - Reduced Ejection (Phase 4)
Aortic and Pulmonic Valves Open; AV Valves Remain Closed
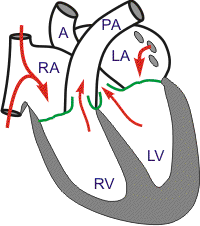
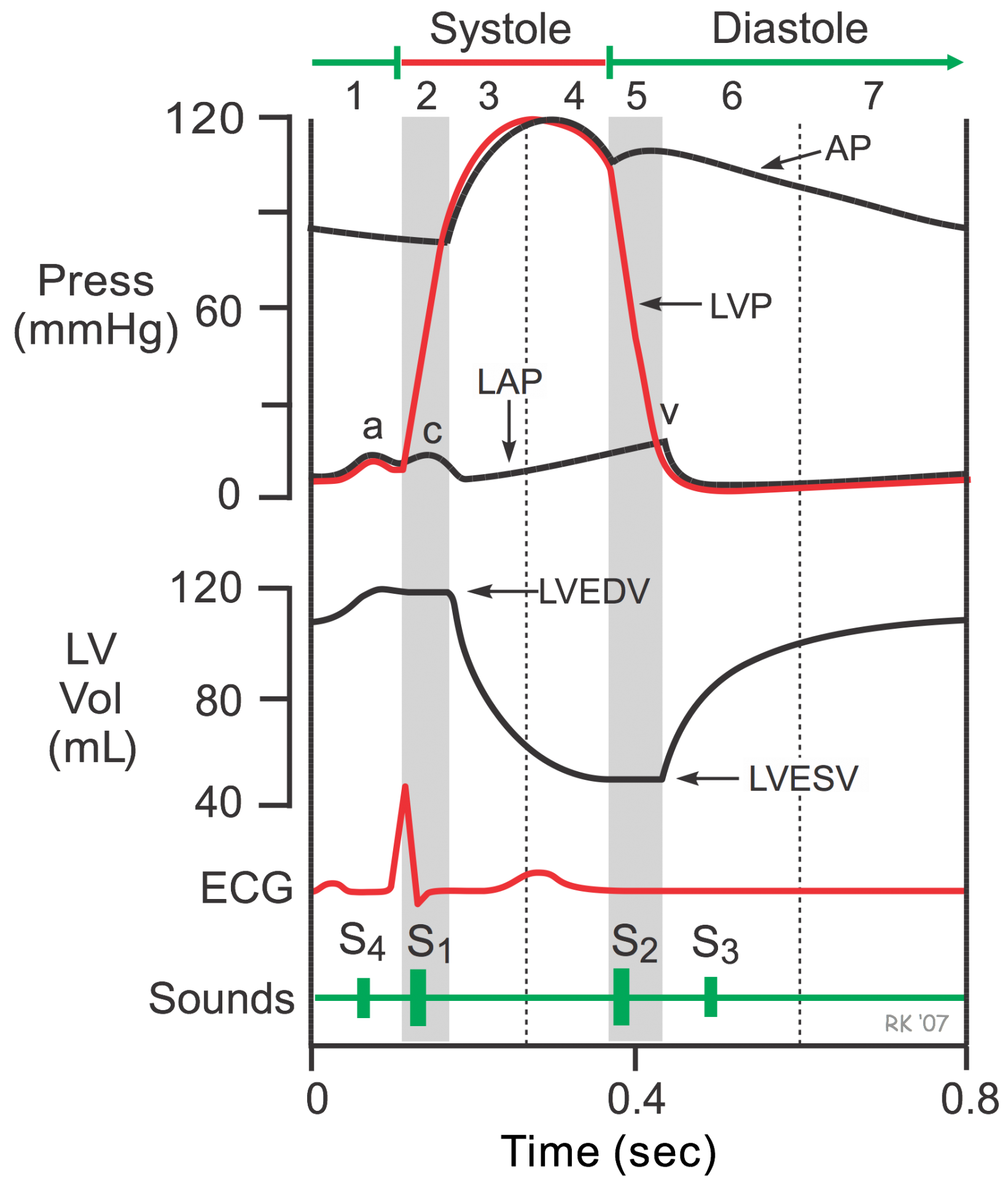 Approximately 200 msec after the QRS and the beginning of ventricular contraction, ventricular repolarization occurs, as shown by the T-wave of the electrocardiogram. Repolarization leads to a decline in ventricular active tension and pressure generation; therefore, the rate of ejection (ventricular emptying) falls. Ventricular pressure falls slightly below the outflow tract pressure; however, outward flow still occurs because of kinetic (or inertial) energy of the blood.
Approximately 200 msec after the QRS and the beginning of ventricular contraction, ventricular repolarization occurs, as shown by the T-wave of the electrocardiogram. Repolarization leads to a decline in ventricular active tension and pressure generation; therefore, the rate of ejection (ventricular emptying) falls. Ventricular pressure falls slightly below the outflow tract pressure; however, outward flow still occurs because of kinetic (or inertial) energy of the blood.
Left atrial and right atrial pressures gradually rise because venous return from the lungs and from the systemic circulation continue to fill those chambers.
Jump to other phases:
- Phase 1 - Atrial Contraction
- Phase 2 - Isovolumetric Contraction
- Phase 3 - Rapid Ejection
- Phase 5 - Isovolumetric Relaxation
- Phase 6 - Rapid Filling
- Phase 7 - Reduced Filling
Revised 11/04/2023
 Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts, 3rd edition textbook, Published by Wolters Kluwer (2021)
Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts, 3rd edition textbook, Published by Wolters Kluwer (2021) Normal and Abnormal Blood Pressure, published by Richard E. Klabunde (2013)
Normal and Abnormal Blood Pressure, published by Richard E. Klabunde (2013)