Reentry
As described elsewhere, conduction blocks can cause bradycardia; however, they can also cause tachycardia. This occurs when impaired conduction leads to a phenomenon termed “reentry.” In fact, this mechanism may account for most tachyarrhythmias found in patients.
Local and Global Reentry
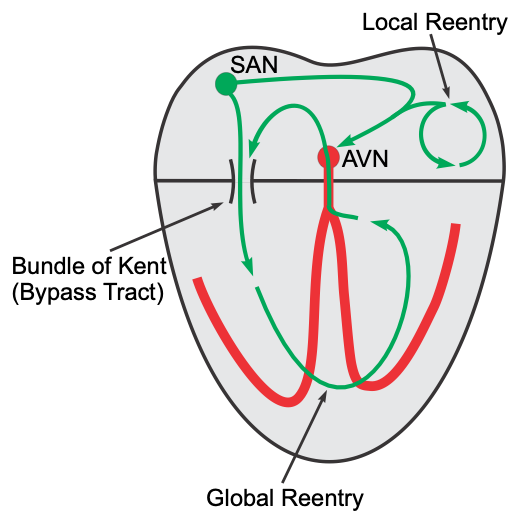 Reentry can occur within a small local region of the heart (local reentry), or it can occur between the atria and ventricles (global reentry). An example of local reentry would be a region within the atrium that becomes a self-perpetuating circuit of excitation. Although the reentry pathway may be localized to a small region, the excitation that is generated can spread throughout the atria by cell-to-cell conduction and lead to atrial tachycardia (a form of supraventricular tachycardia). A local reentry circuit within a ventricle (not shown in the figure) would lead to rapid excitation of the ventricle and ventricular tachycardia. Another example of local reentry is AV nodal reentry (not shown in the figure). In this type of reentry, a circular, self-perpetuating circuit within the AV node generates rapid depolarizations that spread up into the atria and down into the ventricles (AV nodal reentry tachycardia; a common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia).
Reentry can occur within a small local region of the heart (local reentry), or it can occur between the atria and ventricles (global reentry). An example of local reentry would be a region within the atrium that becomes a self-perpetuating circuit of excitation. Although the reentry pathway may be localized to a small region, the excitation that is generated can spread throughout the atria by cell-to-cell conduction and lead to atrial tachycardia (a form of supraventricular tachycardia). A local reentry circuit within a ventricle (not shown in the figure) would lead to rapid excitation of the ventricle and ventricular tachycardia. Another example of local reentry is AV nodal reentry (not shown in the figure). In this type of reentry, a circular, self-perpetuating circuit within the AV node generates rapid depolarizations that spread up into the atria and down into the ventricles (AV nodal reentry tachycardia; a common cause of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia).
Global reentry between the atria and ventricles may involve accessory conduction pathways (“bypass tracts”) such as the bundle of Kent. The AV node is normally the only electrical pathway connecting the atria and ventricles. When accessory pathways exist, impulses can travel between the atria and ventricles by multiple pathways. In the example shown in the above figure, the impulse is traveling through the accessory pathway (bundle of Kent), depolarizing ventricular tissue, then traveling backwards (retrograde) through the AV node to re-excite the atrial tissue and establishing a counter-clockwise global reentry. This type of reentry results in supraventricular tachyarrhythmias (e.g., Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or WPW, found in 0.1% of the population). The figure illustrates a counter-clockwise reentry; however, this reentry can also occur clockwise with orthograde conduction through the AV node and retrograde conduction through the accessory pathway.
Reentry Model
For reentry to occur, certain conditions must be met that are related to:
- The presence of a unidirectional block within a conducting pathway
- Critical timing
- The length of the effective refractory period of the normal tissue
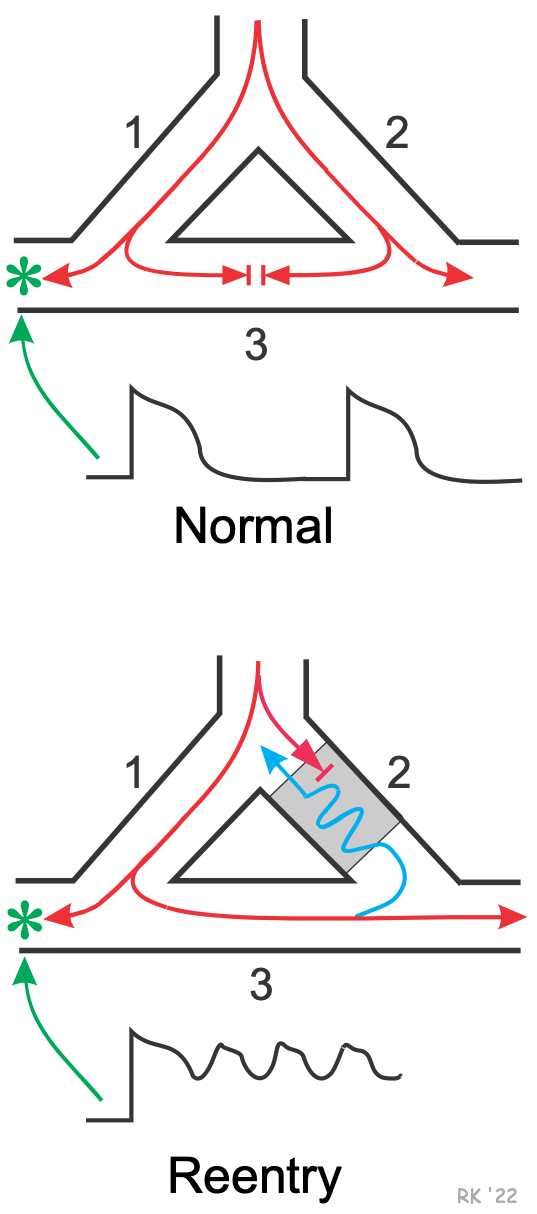 A model for reentry is shown to the left. In normal tissue (top panel of figure), if a single Purkinje fiber forms two branches (1 & 2), the action potential will travel down each branch. An electrode (*) in a side branch from branch 1 would record single, normal action potentials as they are conducted down branch 1 and into the side branch. If branches 1 & 2 are connected by a common, connecting pathway (branch 3), the action potentials that travel into branch 3 will cancel each other out when they meet.
A model for reentry is shown to the left. In normal tissue (top panel of figure), if a single Purkinje fiber forms two branches (1 & 2), the action potential will travel down each branch. An electrode (*) in a side branch from branch 1 would record single, normal action potentials as they are conducted down branch 1 and into the side branch. If branches 1 & 2 are connected by a common, connecting pathway (branch 3), the action potentials that travel into branch 3 will cancel each other out when they meet.
Reentry (bottom panel) can occur if branch 2, for example, has a unidirectional block. In such a block, impulses can travel retrograde (from branch 3 into branch 2) but not orthograde. When this condition exists, an action potential will travel down branch 1, into the common distal path (branch 3), and then travel retrograde through the unidirectional block in branch 2 (blue line). Within the block (gray area), the conduction velocity is reduced because of tissue depolarization. When the action potential exits the block, if it finds the tissue excitable, then the action potential will continue by traveling down (i.e., reentering) branch 1. If the action potential exits the block in branch 2 and finds the tissue unexcitable (i.e., within its effective refractory period, ERP), then the action potential will not be propagated.
Therefore, timing is critical in that the action potential exiting the block must find excitable tissue in order for that action potential to continue to propagate. If it can re-excite the tissue, a circular (counter-clockwise in this case) pathway of high-frequency impulses (i.e., a tachyarrhythmia) will become the source of action potentials that spread throughout a region of the heart (e.g., ventricle) or the entire heart. Because both timing and the refractory state of the tissue are important for reentry to occur, alterations in timing (related to conduction velocity) and refractoriness (related to effective refractory period) can either precipitate reentry or abolish reentry. For this reason, changes in autonomic nerve function can significantly affect reentry mechanisms, either precipitating or terminating reentry. Sympathetic activity decreases the ERP (promoting reentry), whereas vagal activity in the atria and AV node prolongs the ERP (suppressing reentry). Many antiarrhythmic drugs alter the ERP or conduction velocity and alter reentry mechanisms (hopefully abolishing them). For AV nodal reentry tachycardia, drugs that depress AV nodal conduction, such as adenosine, beta-blockers, and calcium channel blockers, are very effective in terminating supraventricular tachycardias that involve reentry circuits.
Revised 2/3/2026
 Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts, 3rd edition textbook, Published by Wolters Kluwer (2021)
Cardiovascular Physiology Concepts, 3rd edition textbook, Published by Wolters Kluwer (2021) Normal and Abnormal Blood Pressure, published by Richard E. Klabunde (2013)
Normal and Abnormal Blood Pressure, published by Richard E. Klabunde (2013)